Chocolate is a hot topic with kidney disease. There is a misconception out there that chocolate is banned and terrible for kidneys. Some people think it is too high in potassium, while others think that it’s too high in phosphorus. At the same time, there is also a lot of research to show the benefits of eating chocolate. We’ll talk through all of this (and more!) in this article.
This post may contain affiliate links through which we may earn a small commission to help keep this website free.
Table of Contents
Types of chocolate
When I searched the ingredient list of all the foods in the USDA database that contain chocolate, I came up with more than 51,000 food products. That’s A LOT of products. I can’t possibly talk through all of those different products, so for the next several sections of this article, I’m going to be referring to plain chocolate.
Chocolate is made from cacao beans. The beans are roasted and turned into a paste. Sometimes the paste is separated into cocoa solids (powder) and cocoa butter. When chocolate is made, they typically mix up varying amounts of cocoa solids, cocoa butter, milk, and sugar.

There are three main types of chocolate:
Dark Chocolate
Dark chocolate is typically made with pure chocolate (the cocoa solids + cocoa butter), and may or may not have some added sugar or other flavors. It typically does NOT contain milk.
Dark chocolate will almost always indicate how much “cacao” or chocolate it contains. The higher the percentage, the less sweet the chocolate will be. Something labeled as 100% Cacao will have zero added sugar.

A chocolate labeled as 70% cacao will be made of 70% chocolate (the cocoa solids and butter) and then 30% of other ingredients (mostly sugar).
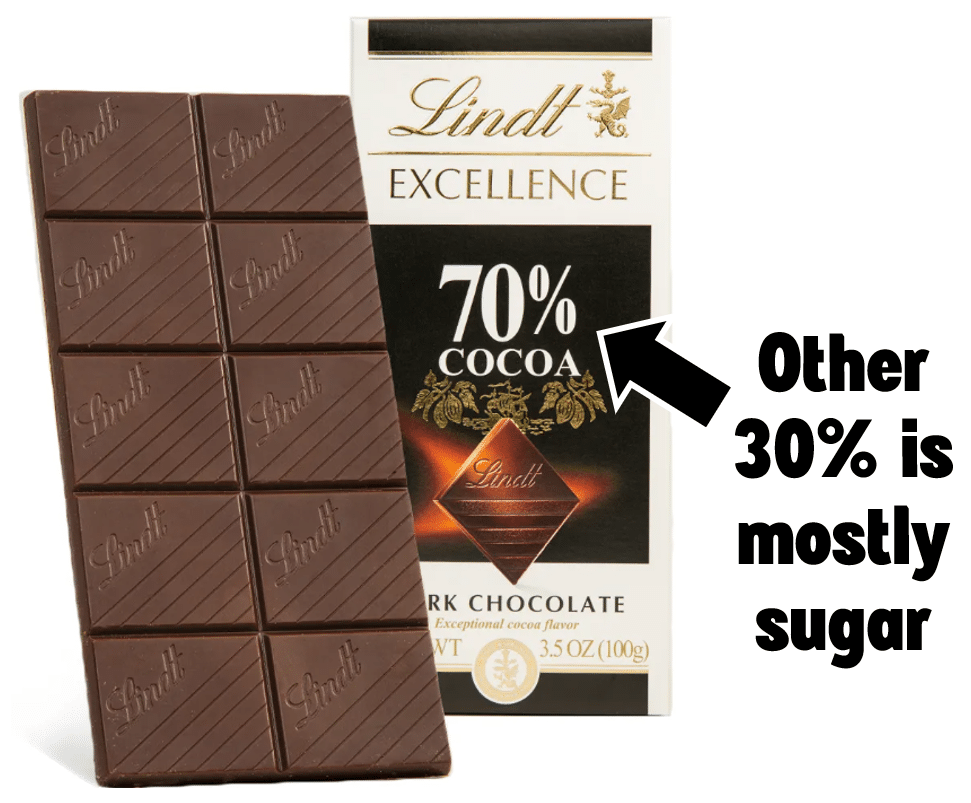
If you’ve ever heard that chocolate is good for you, they were probably talking about dark chocolate (and we will talk about that shortly)
Milk Chocolate
Milk chocolate is made with chocolate (the solids + cocoa butter) as well as milk (hence the name “milk chocolate”) and sugar. Milk chocolate is sweeter than dark chocolate because of the addition of milk and sugar.
Milk chocolate also contains substantially less actual chocolate. In some cases, milk chocolate only contains 10% of actual chocolate, which means that 90% of milk chocolate would be just milk and sugar.
White Chocolate
White chocolate is made of only part of the cacao bean – the cocoa butter. There are not cocoa solids in white chocolate, which is why it is not brown. Similar to milk chocolate, white chocolate will also contain milk, sugar, and possibly some other flavors like vanilla added to it.
Health Benefits of Chocolate
When you hear about the health benefits of chocolate, you are almost always hearing about the health benefits of the cocoa solids from chocolate. Cocoa contains several beneficial compounds called polyphenols.
Polyphenols are found in many plant-based foods including fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, seeds, herbs, and beverages like tea, coffee, and cocoa. Polyphenols have many beneficial effects on the body including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer effects.
The flavonoids, which are a type of polyphenol in cocoa, display a lot of antioxidant capacity. Antioxidants help protect our body’s cells from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals.
By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants contribute to maintaining the balance of our body’s systems and may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, certain cancers, and neurodegenerative conditions.
Cocoa has been extensively researched, and there are many potential benefits associated with consuming cocoa that would be beneficial for people with kidney disease:
- Improvements in the gut microbiome. Researchers have seen increases in health gut bacteria and decreases in harmful gut bacteria from consuming more cocoa.
- Several studies have seen improvements in blood pressure and cholesterol numbers, both common problems in people with kidney disease
- Several studies have seen decreases in markers of inflammation, a common problem in kidney disease
- Several studies have seen improvements in diabetes, such as less hyperglycemia and improved A1C. Diabetes is one of the top two causes of chronic kidney disease.
As you can see, there are many potential benefits to consuming cocoa. An important thing to keep in mind is that the benefits associated with chocolate are specifically related to the cocoa in the chocolate.

What type of chocolate is best for kidney disease?
The more cocoa a chocolate contains , the better. Chocolate that contains less cocoa or no cocoa at all will not have the same beneficial effects. White chocolate contains zero cocoa and milk chocolate is mostly just milk and sugar with very little actual cocoa.
Dark chocolate is the best chocolate for people with kidney disease who want to see the health benefits of eating chocolate because it contains the most cocoa. Dark chocolate is also the best choice for people with diabetes because it will typically have the least amount of sugar and carbohydrate.
However, it is still fine to enjoy other types of chocolate. Even if there are no health benefits to white chocolate or milk chocolate, they are still good for the soul and can make people happy. Just be sure to enjoy it in an appropriate portion size (which we will discuss shortly).

Is chocolate high in phosphorus?
No, chocolate is not a high phosphorus food – as long as it does not contain a phosphorus additive. Plain chocolate does not typically contain any additives, but always check the label to be sure.
Below is a table showing how much phosphorus is in each different type of chocolate. The phosphorus in dark chocolate is all from the cacao bean, which contains phytate. Phytate makes it hard for your body to absorb phosphorus, so your body will only absorb about 30% of the phosphorus in dark chocolate (and maybe less!).
You will see next to the dark chocolate, we show that it has low bioavailability. Even though the 70-85% dark chocolate has the highest amount of phosphorus, it doesn’t end up having the highest amount of absorbable phosphorus because it is plant based and your body just can’t absorb it that well.
The phosphorus in milk chocolate and white chocolate comes mostly from milk. The phosphorus in milk is a little easier to absorb, but your body still cannot absorb it all.
To better understand phosphorus bioavailability and phosphorus additives, watch our video here.
| Type of chocolate | Phosphorus per ounce | Bioavailability | Absorbable Phosphorus |
| Dark chocolate – 45-59% cacao | 58mg | Low – 30% | 17mg |
| Dark chocolate – 60-69% cacao | 74mg | Low – 30% | 22mg |
| Dark chocolate – 70-85% cacao | 87mg | Low – 30% | 26mg |
| Milk Chocolate | 59mg | Medium – 60% | 35mg |
| White chocolate | 50mg | Medium – 60% | 30mg |
Is chocolate high in potassium?
No. Chocolate is not high in potassium. Certain chocolate products may be high in potassium, but plain old chocolate is not considered a high potassium food. Below is a table showing the different types of chocolate and how many calories and how much potassium is in an ounce of each chocolate:
| Type of chocolate | Calories per ounce | Potassium per ounce |
| Dark chocolate – 45-59% cacao | 155 | 158mg |
| Dark chocolate – 60-69% cacao | 164 | 161mg |
| Dark chocolate – 70-85% cacao | 170 | 203mg |
| Milk Chocolate | 152 | 105mg |
| White chocolate | 153 | 81mg |
In general, I consider a food to definitely be low in potassium if there are fewer mg of potassium than there are calories. However, even the highest potassium chocolate listed on the table – the 70-85% cacao dark chocolate – is still not that high in potassium.
Let’s say that hypothetically you decided to ONLY eat chocolate one day (and I am definitely NOT recommending this. This is just a hypothetical). If you ate 12 ounces of that dark chocolate, you would eat 2,040 calories and 2,436mg of potassium.
The daily value for potassium is 4,700 mg, so the dark chocolate diet would have you at HALF of the daily value for potassium. That’s really low!
Again, this is just a hypothetical to illustrate that chocolate is definitely NOT high in potassium.
I also just want to mention that there are a lot of reasons that potassium can get out of balance in kidney disease that are not related to the actual quantity of potassium that you are eating, so don’t restrict foods that are high in potassium unless you’ve been instructed to do so by your doctor or dietitian.
Portion Size of Chocolate
After giving the hypothetical example of only eating chocolate in a day, we should probably discuss what an ideal serving size of chocolate is.
Despite all of the benefits of eating dark chocolate, it isn’t a perfect food, and we do need to be mindful of our portions.
Most chocolate that people actually enjoy eating contains sugar. Even if you do not have diabetes, too much sugar is not good for your health. Too much sugar is linked to many chronic diseases including gout, fatty liver disease, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, high cholesterol, and dental disease – just to name a few.
Additionally, eating a lot of sugary foods means that you have less room to eat more healthful foods like fruits, vegetables, nuts, beans, and whole grains. We know that eating more plant foods, especially fruits and vegetables is really important for people with kidney disease. And if you are on dialysis, you have higher protein needs and chocolate will not have enough protein in it to meet your needs for the day.
By enjoying treats like chocolate in moderation, we can still get in adequate fruits and vegetables.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends that individuals limit their sugar to no more than 10% of their daily calories. To keep things simple, I usually tell people to limit their sweet treats to 200 calories a day.
For chocolate, 200 calories would be a little over an ounce of chocolate. An ounce of dark chocolate also happens to be an amount that was used in a lot of different studies on the benefits of dark chocolate, so eating an ounce of dark chocolate is definitely enough to experience some of the benefits.
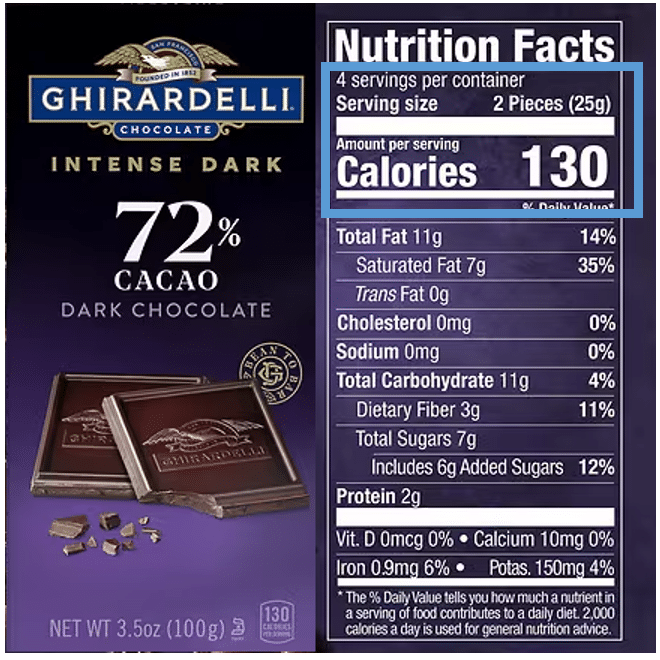
To figure out the right portion size, just read the food label. For example, let’s look at the dark chocolate squares. The nutrition label lists a serving size as 2 squares, which is 130 calories. This is definitely less than 200 calories, so that’s great. If the label showed more than 200 calories per serving, then you would know to eat a bit less than what is calls a serving.
Is chocolate high in oxalates?
Yes, chocolate is high in oxalates. If you are prone to kidney stones, you may need to limit your intake of chocolate.
Other ways to eat chocolate
So far, we’ve mostly talked about plain chocolate. However, there are thousands of different food items that you can eat that contain chocolate, and I’m going to briefly go through some of them here.
Is cocoa powder okay for kidney disease?
It depends on how it is used. Pure cocoa powder is high in potassium and phosphorus. Chocolate is made of cocoa solids (powder) plus cocoa butter. Cocoa butter contains no phosphorus or potassium, so it balances out the high potassium and phosphorus in cocoa powder to make chocolate an overall low phosphorus and low potassium food.
When cocoa powder is mixed with water or milk to make hot chocolate, this will often result in a high potassium beverage (Note: most products that are marketed as hot cocoa mix will contain phosphorus additives which would make those drinks high in phosphorus). However, when cocoa powder is used in recipes that call for a lot of added fat (oil or butter), the final product is typically not considered high in potassium or phosphorus.
Are Brownies okay for kidney disease?
Yes, brownies are a good example of how to use cocoa powder in a recipe and end up with a low potassium, low phosphorus food. Brownies are typically a good option if you are craving something sweet and chocolate-y.
Brownie mixes rarely contain phosphorus additives because brownies do not typically call for baking powder, as you can see in the ingredient list below. Baking powder is a phosphorus additive and can add a significant amount of phosphorus to a food. Homemade brownies are an excellent choice.

Pre-made brownies may be more likely to contain phosphorus additives, so always check the food labels.
Since brownies are not a significant source of cocoa, there are no expected benefits to eating a brownie outside of the pleasure you get from eating them.
Be sure to limit your portion size to a small 200 calorie brownie. A 200 calorie brownie would have an estimated 75mg of potassium and less than 57mg of phosphorus, which would be naturally occurring and poorly absorbed.
Are cookies okay for kidney disease?
Cookies are another good option for a sweet treat. Cookies do not usually have baking powder in them. Baking powder is a phosphorus additive and can add a significant amount of phosphorus to a food. Some pre-made cookies may be high in sodium or contain additives though, so always check food labels. You can also check out our list of Kidney Friendly Cookies.
Since cookies are not a significant source of cocoa, there are no expected benefits to eating cookies outside of the pleasure you get from eating them.
Be sure to limit your portion size to 200 calories of cookie or less.
Is chocolate cake okay for kidney disease?
Cake almost always contains baking powder, so the majority of cakes are high in phosphorus (regardless of whether they are chocolate or not). In the example below, you can see that there are three different phosphorus additives listed, although the potassium listed on the food label is quite low (2% is only about 94mg of potassium).

Also, maybe you noticed that I featured a Betty Crocker brownie mix earlier in this article, which was kidney friendly, while this Betty Crocker cake mix is not kidney friendly. It’s not about the brands, it’s about the individual products. Just because one product from a particular brand was kidney friendly doesn’t mean they all will be. You have to read labels.
If you are baking a cake from scratch, you can make your own kidney friendly baking powder using 2 parts cream of tartar and 1 part baking soda. If you use this kidney friendly baking powder, then chocolate cake is kidney friendly.
We have also identified a few kidney friendly boxed cake mixes that you can try if you go to our Kidney Friendly Cake Mixes page.
As always, be sure to limit your portion size to 200 calories of cake (about the size of an average cupcake). Since cake is not a significant source of cocoa, there are no expected benefits to eating cake outside of the pleasure you get from eating it.
Is chocolate ice cream okay for kidney disease?
Yes, however chocolate ice cream will typically be higher in potassium than vanilla because of the added cocoa powder. If you compare the ingredients for this chocolate and vanilla ice cream, you’ll see that one of the only differences in the ingredients is the cocoa powder, and since we know cocoa powder is a high potassium food, it is not surprising that the chocolate is higher in potassium.

A 200 calorie portion of chocolate ice cream would not be considered high in potassium though. Since ice cream is not a significant source of cocoa, there are no expected benefits to eating chocolate ice cream outside of the pleasure you get from eating them, so be sure to limit your portion size.
Always check the ingredient label to see if there are phosphorus additives in your ice cream. There are many ice cream flavors that do not contain additives, but there are also many that do. We also recommend buying full fat ice cream. Products that are reduced fat or “light” are typically more likely to contain a phosphorus additive.
Is chocolate candy okay for kidney disease?
Yes. Be sure to check ingredient labels to ensure that there are no phosphorus additives. Chocolate candy that contains caramel is the most likely to have a phosphorus additive, so you would want to avoid those.
Most candy will be made of milk chocolate, which is not a significant source of cocoa. There are no expected benefits to eating a milk chocolate candy outside of the pleasure you get from eating it, so be sure to limit your portion size to 200 calories or less so that we don’t overeat candy.
Below are a few brands of candy that do not typically contain phosphorus additives. This is not a complete list. There are 100s (maybe 1000s) of types of chocolate candy out there. Too many for us to review!

Note that many of these candies come in packages that are more than 200 calories, so be sure to eat less than the whole package, or choose smaller, “fun size” packages.



